If you have trouble sleeping, you may have heard about red light therapy. This light therapy uses low levels of red or near-infrared light and has shown promise in enhancing sleep quality. Understanding how it works means exploring its impact on critical sleep-regulating factors. For instance, does red light produce melatonin to make falling asleep easier?
Red light therapy for sleep may make falling asleep easier by regulating the sleep-wake cycle, potentially leading to more consistent and restorative sleep. So, does red light help you sleep? Keep reading to find out.
- What Is Red Light Therapy?
- How Does Red Light Help You Sleep?
- What Are the Differences Between Red Light vs. Blue Light?
- How Can You Use Red Light Therapy for Sleep?
- What Are Additional Benefits of Red Light Therapy?
- What Are Other Tips for Improving Sleep?
- Wrapping Up: Does Red Light Help You Sleep?
What Is Red Light Therapy?
Red light therapy exposes you to low levels of red or near-infrared light to simulate various responses in the body. This non-invasive therapy has potential benefits across a wide range of applications, including skin health, pain management, and sleep improvement.
Red light therapy uses the therapeutic properties of specific wavelengths of light to penetrate the skin, interacting with cells. These wavelengths are absorbed by the mitochondria, triggering a cascade of reactions in the body.
Red light sleep, in particular, is believed to impact melatonin production and regulate the body’s circadian rhythm, both of which are crucial for maintaining healthy sleep patterns.
Light, in general, affects the sleep-wake cycle. The human body’s internal clock is highly sensitive to light cues. Exposure to natural light during the day helps us feel alert and awake. Conversely, reduced exposure to light in the evening signals the body to produce melatonin, a hormone that induces sleepiness and prepares the body for rest.
How Does Red Light Help You Sleep?
One of the best benefits of red light before bed is its impact on sleep. Red light can influence sleep quality by affecting two key physiological mechanisms: melatonin secretion and circadian rhythm.
Melatonin is a hormone produced in response to darkness, signaling to the body that it’s time to fall asleep. Exposure to light, particularly blue light from smartphones and electronics, inhibits melatonin secretion, delaying the onset of sleep.
However, red light has been shown to have a lesser impact on melatonin suppression compared to blue or white light. Red light is less disruptive to the body’s internal clock. Unlike blue or white light, which can suppress melatonin production and shift circadian rhythm, red light has been found to have minimal disruptive effects.
Simply put, when exposed to red light, especially in the evening hours, the body’s production of melatonin may remain relatively unaffected, allowing for the natural progression towards the beginning of sleep.
But does red light produce melatonin? A study found that 14-day red light therapy significantly improved sleep quality and serum melatonin levels, improving sleep quality. Therefore, it’s possible that red light can promote the appropriate release of melatonin and synchronize the body’s internal clock to facilitate the transition to sleep and help you fall asleep faster.
Overall, red light appears to stimulate melatonin production or have minimal disruptive effects on its secretion, which is crucial for establishing and maintaining healthy sleep cycles.
What Are the Differences Between Red Light vs. Blue Light?
Red light and blue light have distinct effects on sleep patterns and melatonin production due to their different wavelengths and interactions with the body’s circadian rhythm. Let’s take a look at the key differences between red light vs. blue light:
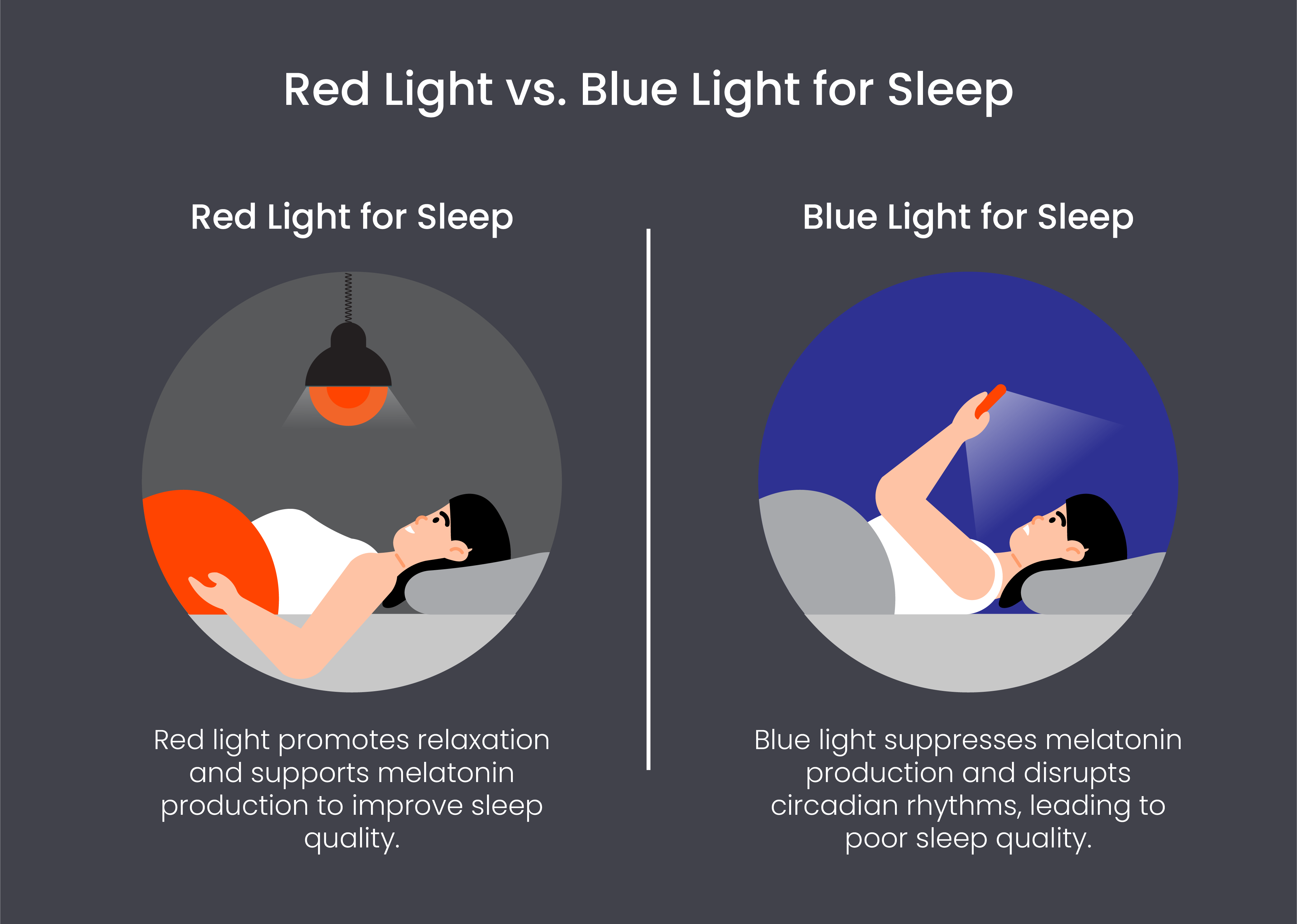
- Wavelengths: Red light has longer wavelengths than blue light. It falls within the range of 620 to 750 nanometers on the electromagnetic spectrum. On the other hand, blue light has shorter wavelengths and falls within the range of 450 and 495 nanometers.
- Effect on circadian rhythm and melatonin production: Exposure to red light before bedtime has been shown to have minimal impact on melatonin production. Unlike blue light, which suppresses melatonin secretion, red light is less disruptive to the body’s sleep-wake cycle. There are plenty of negative effects of blue light on sleep. For instance, blue light can significantly suppress melatonin, delaying the onset of sleep and disrupting the circadian rhythm, leading to difficulties falling asleep and poorer sleep quality overall.
- Effect on circadian rhythm and melatonin production: Exposure to red light before bedtime has been shown to have minimal impact on melatonin production. Unlike blue light, which suppresses melatonin secretion, red light is less disruptive to the body’s sleep-wake cycle. There are plenty of negative effects of blue light on sleep. For instance, blue light can significantly suppress melatonin, delaying the onset of sleep and disrupting the circadian rhythm, leading to difficulties falling asleep and poorer sleep quality overall.
- Eye health: Red light is generally considered less harmful to the eyes because it has longer wavelengths and lower energy levels, meaning it penetrates less deeply into the eye. On the other hand, blue light can potentially contribute to eye strain and digital eye fatigue.
- Mood and cognitive effects: Because red light can enhance sleep quality, it may improve mood and cognitive performance. At the same time, blue light exposure can have positive effects on mood, alertness, and cognition because it regulates the body’s circadian rhythm to promote wakefulness.
How Can You Use Red Light Therapy for Sleep?
Incorporating red light for sleep into your nighttime routine can improve your sleep quality. Here’s how to use red light therapy for sleep at home:
- Select the best red light therapy devices: When shopping, look for devices designed for red light therapy. These include red light therapy panels, lamps, or bulbs. Consider the size and coverage area of the device to ensure it can illuminate your sleeping environment.
- Optimize exposure times: Aim for consistent exposure to red light therapy each night, ideally before bedtime. This can help signal to your body that it’s time to start preparing for sleep.
- Use it as a night light: Include red light therapy as a calming element in your bedtime routine. Dim the lights in your room and switch on your red light therapy device to create a soothing atmosphere.
- Incorporate it into your routine: Consider incorporating red light therapy into your overall sleep hygiene routine, which may include practices like maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing and comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities before bed.
What Are Additional Benefits of Red Light Therapy?
Let’s go beyond the benefits of red light before bed. Red light therapy offers benefits beyond its potential for improving sleep quality. Research has shown that red light can positively impact various aspects of health and well-being, offering benefits such as:
- Improved skin health: Red light therapy can enhance skin health by stimulating collagen production, improving skin elasticity, and reducing signs of aging.
- Pain relief and inflammation: Studies have shown that red light therapy can provide effective pain relief and reduce inflammation in various conditions, including arthritis, musculoskeletal disorders, and chronic pain syndromes.
- Faster wound healing: Red light therapy has been found to accelerate the wound healing process by stimulating tissue regeneration, promoting the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis), and reducing inflammation.
- Enhanced muscle recovery and performance: Athletes can benefit from red light therapy’s ability to enhance muscle recovery, reduce exercise-induced muscle fatigue, and improve athletic performance.
What Are Other Tips for Improving Sleep?
Improving sleep is essential for your overall health. While incorporating red light therapy into your sleep routine can be beneficial, there are several other ways to improve your sleep, including:
- Create a comfortable sleep environment: Ensuring your bedroom is a haven for rest is crucial for achieving quality sleep. Consider the temperature, amount of light, and noise in your room. You can use earplugs or a white noise machine, along with blackout curtains, to help create a tranquil sleep environment. Additionally, invest in quality bedding that provides optimal comfort for your body, allowing you to fully unwind.
- Invest in the right mattress: Your mattress significantly affects your sleep quality and overall comfort. Whether you choose a memory foam mattress or a hybrid mattress, it should align with your specific needs and preferences. Consider factors like the mattress material, firmness level, and motion isolation to help you find the perfect fit.
- Limit screen time before bed: Using your phone before bed can keep you up at night. Electronics emit blue light, which can interfere with your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, making it harder to fall asleep. To promote better sleep, establish a digital curfew by limiting screen time at least an hour before bedtime. Instead, opt for calming activities like reading, gentle stretching, or listening to calming playlists for sleep.
- Exercise regularly: Exercising throughout the day can improve sleep quality by reducing stress and anxiety accumulated throughout the day. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise five days or more a week. However, you might want to consider avoiding exercise too close to bedtime, as it may energize you and make it difficult to fall asleep.
- Promote sleep hygiene: Establishing healthy sleep habits and routines is essential for achieving constant and restorative sleep. Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day. You can also create a calming bedtime routine to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down.
- Avoid alcohol and caffeine: Caffeine is a stimulant that can disrupt sleep and make it difficult to fall asleep. On the other hand, alcohol, although sedating, can lead to fragmented and less restorative sleep later in the night. Limit your consumption of these beverages, especially in the afternoon and evening hours, to help you sleep better. Consider these foods with melatonin as a nighttime snack to help you sleep better.
- Plan naps accordingly: Napping can be a great way to recharge and combat daytime sleepiness, but you should nap strategically to avoid interfering with your sleep schedule. Keep naps short and schedule them earlier in the day to prevent them from disrupting your ability to fall asleep at night.
Wrapping Up: Does Red Light Help You Sleep?
Red light therapy for sleep may help improve your sleep quality by positively impacting melatonin secretion and regulating your body‘s circadian rhythm. By incorporating red light therapy into your sleep routine, you may experience more consistent and restorative sleep.
At Layla, we understand the importance of quality sleep, which is why we offer a range of products designed to enhance your sleep experience. From our comfortable bedding and supportive mattress to our memory foam pillows, we’re dedicated to helping you achieve the best possible sleep night after night. Explore our collection today and take the first step toward better sleep.



